AP Psychology Unit 5 Notes: Mental and Physical Health
January 27, 2025

Get ready for the AP Psychology exam with Barron's free AP Psychology study notes. These notes should be used to supplement what you’re learning in your AP Psych class. You will find most of the content from this unit in two chapters in the textbook you use for your AP class: psychological disorders and treatment. More study strategies and expert tips can be found in our new AP Psychology prep book.
[ READ NEXT: Top 5 Study Tips for the AP Psychology Exam ]
AP Psychology: Unit 5 Summary
This unit addresses psychological disorders and treatment of mental health issues as well as their opposite: psychological health. Although there are many types of psychologists, including social psychologists, developmental psychologists, and cognitive psychologists, the largest group of psychologists are clinicians. Clinical psychologists are concerned with how psychological disorders are defined and diagnosed and with what treatments are recommended for these disorders.
AP Psychology: Unit 5 Key Terms
Below, we describe some of the key terms you should review ahead of the AP Psychology exam.
- Eustress: When stress is positive and motivating.
- Distress: When stress is negative and debilitating
- General Adaption Syndrome: Hans Selye’s general adaptation syndrome (GAS) describes the general response humans and other animals have to a stressful event. Our response pattern to many different physical and emotional stressors is very consistent.
- Virtues: Positive psychology researchers investigate how aspects of personality they call character strengths or virtues can be measured and how using these strengths relates to life satisfaction and achievement. These researchers identify six core virtues that seem to be valued across all major religions and philosophies: wisdom, courage, humanity, justice, temperance, and transcendence.
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM): The American Psychiatric Association uses the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). The DSM, as its name suggests, provides a way for psychologists to diagnose their patients. The DSM-5, which is the most recent edition, contains the symptoms of everything currently considered to be a psychological disorder.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: Children with autism spectrum disorder seek out less social and emotional contact than do other children and are less likely to seek out parental support when distressed. In addition, people with autism spectrum disorder tend to be hypersensitive to sensory stimulation.
- Anxiety disorders: Anxiety disorders, as their name suggests, share a common symptom of anxiety. Three common anxiety disorders are phobias, generalized anxiety disorder, and panic disorder.
- Somatic symptom disorders: Somatic symptom disorders occur when a person manifests a psychological problem through a physiological symptom. In other words, such a person experiences a physical problem in the absence of any identifiable physical cause.
- Dissociative disorders: Dissociative disorders involve a disruption in conscious processes. Dissociative amnesia and dissociative identity disorder (DID) are classified as dissociative disorders.
- Major depressive disorder: Major depressive disorder, also known as unipolar depression, is the most common mood disorder and is often referred to as the common cold of all psychological disorders. The DSM-5 outlines the symptoms that must be present for such a diagnosis. One key factor is the length of the depressive episode. People who are clinically depressed remain unhappy for more than two weeks in the absence of a clear reason.
- Bipolar disorder: Unlike unipolar depression, bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic depression, usually involves both depressed and manic episodes. The depressed episodes involve all the symptoms discussed above. People experience manic episodes in different ways, but they usually involve feelings of high energy. Some sufferers feel a heightened sense of confidence and power, while others simply feel anxious and irritable.
- Schizophrenia spectrum disorders: Schizophrenia spectrum disorders are probably the most severe and debilitating of the psychological disorders. They tend to strike people who are entering young adulthood. The fundamental symptom of schizophrenia is disordered, distorted thinking often demonstrated through delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, disorganized speech, and/or disorganized motor behavior.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder: Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is when persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) cause someone to feel the need (compulsion) to engage in a particular action.
- Psychodynamic theory: Psychodynamic therapy grew out of Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic approach. Psychoanalysis is a therapeutic technique developed by Sigmund Freud. A patient undergoing traditional psychoanalysis will usually lie on a couch while the therapist sits in a chair out of the patient’s line of vision. Psychodynamic theorists view the cause of disorders as unconscious conflicts. As a result, their focus is on identifying the underlying cause of the problem.
- Applied behavioral analysis: One behavioral approach, most used to help people with developmental disorders like autism spectrum disorder, is known as applied behavior analysis (ABA). Therapists trained in ABA set up systems of reinforcement to help teach their clients how to be successful in the world.
- Cognitive therapy: As cognitive therapists locate the cause of psychological problems in the way people think, their methods of therapy concentrate on changing these unhealthy thought patterns. The goal of cognitive therapy is often referred to as cognitive restructuring, which involves challenging people’s patterns of maladaptive thinking. Cognitive therapy is often quite combative as therapists challenge the irrational thinking patterns of their clients.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy: One popular group of therapies combines the ideas and techniques of both cognitive and behavioral psychologists. This approach to therapy is known as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
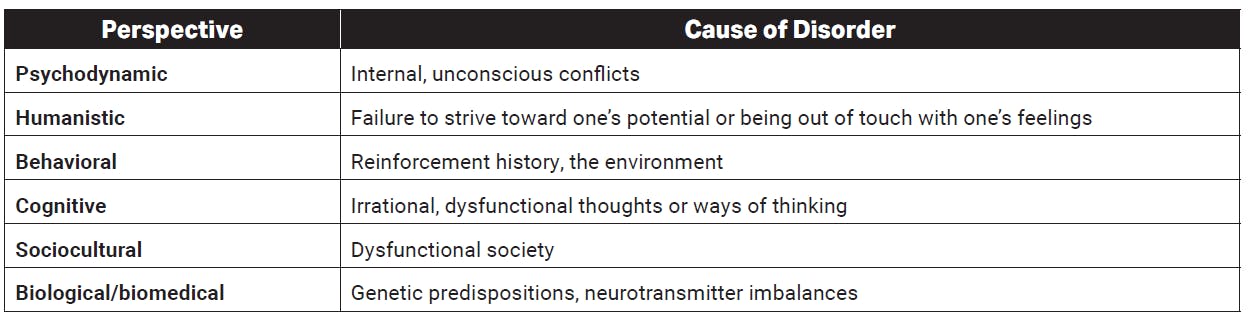
Different Perspectives on the Causes of Psychological Disorders
The table below showcases the different perspectives on the causes of psychological disorders you should review for the AP Psychology exam.
AP Biology Resources
- About the AP Biology Exam
- Top AP Biology Exam Strategies
- Top 5 Study Topics and Tips for the AP Biology Exam
- AP Biology Short Free-Response Questions
- AP Biology Long Free-Response Questions
AP Psychology Resources
- What’s Tested on the AP Psychology Exam?
- Top 5 Study Tips for the AP Psychology Exam
- AP Psychology Key Terms
- Top AP Psychology Exam Multiple-Choice Question Tips
- Top AP Psychology Exam Free Response Questions Tips
- AP Psychology Sample Free Response Question
AP English Language and Composition Resources
- What’s Tested on the AP English Language and Composition Exam?
- Top 5 Tips for the AP English Language and Composition Exam
- Top Reading Techniques for the AP English Language and Composition Exam
- How to Answer the AP English Language and Composition Essay Questions
- AP English Language and Composition Exam Sample Essay Questions
- AP English Language and Composition Exam Multiple-Choice Questions
